Python, being one of the most popular programming languages for data analysis, offers a wide range of libraries and tools to work efficiently with datasets.
Here in this post, we will explore how to load, view, and manipulate datasets in Python using the pandas library, one of the most powerful and flexible tools for data analysis.
How to Access Dataset in Python
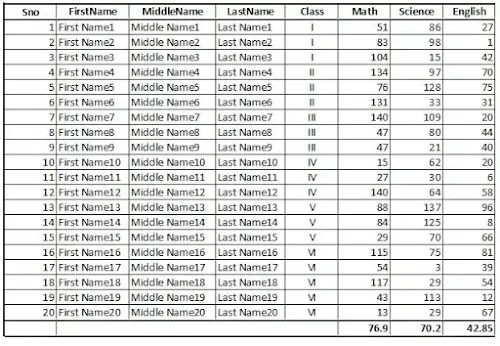 |
| How to Access Dataset in Python |
Getting Started
A dataset in python is a structured collection of data. It often comes in the form of tables (like Excel files or CSV files), where each row is an observation and each column is a variable or attribute.
For example, a dataset of students might contain columns such asName, Age, Grade, and Major.
Dataset Type in Python
There are 6 data set in python, a python dataset can come in various types depending on the context in which you're working. Here’s a breakdown of common dataset types in Python:
- List of Dictionaries: Used for small datasets, especially in vanilla Python.
- Pandas DataFrame: Used for structured data (like CSV files or databases).
- NumPy Arrays: Used for numerical datasets, especially for machine learning and scientific computing.
- PyTorch Dataset: For deep learning tasks using PyTorch.
- TensorFlow Dataset: For use in TensorFlow pipelines.
- CSV or JSON Files: Often datasets are loaded from external files
Loading Dataset in Python
import pandas as pd
# Load dataset
df = pd.read_csv('students.csv')
# Show the first five rows
print(df.head())
This will load the CSV file into a DataFrame, which is a two-dimensional labeled data structure provided by pandas.
Pandas
Pandas is a very popular and most widely used library for data exploration and presentation, it provides DataFrame for loading and presenting data in the structure.
Pandas DataFrame can be used for loading, filtering, sorting, grouping, and joining dataset, more it also supports for dealing with missing data. Pandas library provided different methods for loading data from dataset or files.
Pandas is an open-source data analysis tool for Python programming language, which is easy to use in a structure, analyze, and present data. It is a highly-performed, popular, and most widely used library.
DataFrame
A DataFrame is a very efficient two-dimensional flat data structure and arranging data in rows and columns. The rows and columns can be an index or name. It can be imagined as a table in SQL. The data frame is inherited into Python by the Pandas library, hence this DataFrame is commonly known as Pandas DataFrame.
Characteristics of Pandas DataFrame
- Pandas DataFrame is a highly performed and efficient DataFrame object for data manipulation with integrated indexing.
- It is a tool for reading and writing data between in-memory data structures and different formats: CSV and text files, Microsoft Excel, SQL databases, and the fast HDF5 format. Pandas Library provides the below method for the loading dataset.
read_csvto read comma separated values.read_jsonto read data with JSON format.read_excelto read excel file.read_tableto read database tables.read_fwfto read data with the fixed-width format.
- Flexible reshaping and pivoting of data sets.
- Intelligent data alignment and integrated handling of missing data.
- Intelligent label-based slicing, fancy indexing, and subsetting of large data sets.
- Aggregating or transforming data with a powerful group by engine allowing split-apply-combine operations on data sets.
- High-performance merging and joining of data sets.
- Columns can be inserted and deleted from data structures for size mutability.
To use pandas in python, the pandas module needs to be imported into the environment using the import keyword. The Pandas method can be invoked using the format pandas.method name (pandas.read_cvc). Instead of using Pandas full name, the library can be imported using alias like the below code and the same alias can be used to invoke pandas methods as well.
Import pandas as pdf
In the above code, the pandas library is imported as alias pdf.
Installing Pandas Library
Pandas can be installed through conda-forge and PyPI as well. Here the below commands to install pandas.
Install Panda via conda conda install pandas
pip install pandas
Note that the Package Manager tool(pip) must have installed in your machine, follow the below steps to install the Pandas library.
- Press Windows Key+R key.
- Enter cmd.exe and press Enter.
- The command prompt will appear.
- Use the above appropriate command and press Enter.
- The installation process will be started, if everything going fine the package or module will be installed successfully.
Loading Python Datasets
Usingread_excel
The below example reads an excel sheet from 'D' drive, loads data from sheet1 into Pandas DataFrame and prints in the screen.
# Demonstration for Reading and Loading data from excel
# Importing Pandas library
import pandas as xl
#Loading data from excel
data = xl.read_excel (r'D:\pandas.xlsx', sheet_name='Sheet1')
#Displaying data in the screen
print (data)
The read_excel takes first parameter as full name of excel sheet and second parameter is sheet name to be read. Note that the first row of excel file is expected as header of dataset.
read_csv
The below example access dataset of cvc file using read_csv method.
# Demonstration for Reading and Loading data from excel
# Importing Pandas library
import pandas as xl
#Loading data from cvc
data = xl.read_cvc (r'D:\pandas.csv')
#Displaying data in the screen
print(data)
read_csv takes the file name as parameter, it uses comma as separator. If any other separator uses then parameter sep to be set to appropriate character. The first line in the dataset is expected to be header. if no header is there in dataset then the header parameter needs to be set to none.
read_json
# Demonstration for Reading and Loading data from excel
# Importing Pandas library
import pandas as xl
#Loading data from cvc
data = xl.read_json (r'D:\pandas.json')
#Displaying data in the screen
print(data)
Access Dataset in Python
Exploring the Dataset
Once loaded, you can explore the dataset. These methods help you understand the size, structure, and quality of the data.
# Get summary info
print(data.info())
# Get basic statistics
print(data.describe())
# Check for missing values
print(data.isnull().sum())
Manipulating Data
Python makes it easy to manipulate datasets. Here are some common operations:
Selecting Columns # Select the 'Name' column
names = data['Name']
# Filter students older than 20
older_students = data[data['Age'] > 20]
# Add a new column based on a condition
df['Passed'] = data['Grade'] >= 60
# Group by 'Major' and calculate average grade
avg_grades = data.groupby('Major')['Grade'].mean()
data.to_csv('students_updated.csv', index=False)
Related Articles
- Read Excel data using Pandas DataFrame
- Python Connect to SQL Database
- How to install pyodbc window
- Install mysql for Python
- PIP Install on Windows
- Installing Python
Summary
Python’s simplicity and powerful libraries like pandas make it an ideal language for data analysis. Whether you're cleaning messy data, generating reports, or building machine learning models, mastering datasets in Python is a valuable skill.
Thanks
